Manufacturing Digital Transformation (Industry 4.0)
Capability analysis of the company
Digital manufacturing is an integrated approach to manufacturing that is centered around a computer system. The transition to digital manufacturing has become more popular with the rise in the quantity and quality of computer systems in manufacturing plants. Overall, digital manufacturing can be seen sharing the same goals as computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM), flexible manufacturing, lean manufacturing, and design for manufacturability (DFM). The main difference is that digital manufacturing was evolved for use in the computerized world.
There are three important interacting development areas which importance is in direct correlation with the business strategy (make to order, customized manufacturing, make to stock) of the company.
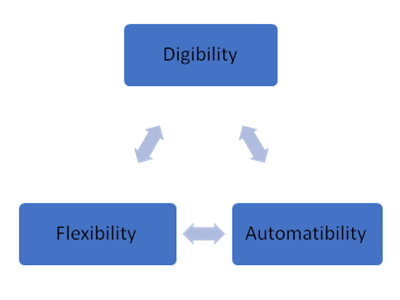
Digibility is the level of digitization the manufacturing, that is the level of implementation of various digital techniques in the extending supply chain (marketing, R&D, purchasing, process planning, manufacturing, testing, logistics, selling, after-sale services, recycling).
Flexibility means to produce reasonably priced customized products of high quality that can be quickly delivered to customers. There are different meanings of flexibility: machine flexibility, operation flexibility, volume flexibility, routing flexibility, process flexibility, product flexibility, expansion flexibility.
Automatibility emphasis to the level of use different automation tools (CNC, robotics, material handling systems, etc) in manufacturing operations.
Self estimation principles
Self estimation is a real-time engineering aid to the company to be more effective and sustainable. Self estimation means to have current understanding about the existing situation and real needs in a company in a certain field. The estimation procedures have a meaning of audit.
The aim of a digiaudit is to get an overview of the extent to which and for what purpose companies are using different digitizing instruments in their value chain.
Working out the principles of Digiaudit the horizontal (manufacturing processes) and vertical (order fulfilling process) value chain of a company has been taken into consideration. In these value chains different processes business planning, customer relationship management, manufacturing operations and control, supply chain management, etc) in different company levels could be digitized. The bases for Digiaudit structure was US Standard ANSI/ISA 95.00.xx (or corresponding ISO standard ISO/IEC 62264-xx).
Digiaudit covers the following most important areas in manufacturing:
| Name | Digitalization Field |
|---|---|
| CRM | Customer Relationship System |
| ERP | Enterprise Resource Planning |
| PLM | Product Lifecycle Management |
| MES | Manufacturing Execution System |
| IoT | Vertical and Horizontal Value Chain Integration |
| CPS | Cyber Physical Systems |
| CAQ | Computer Aided Quality Control |
| WMS | Warehouse Management System |
| CMMS | Computerized Maintenance Management System |
| LIMS | Laboratory Information Management System |

